Unlock the Secrets of Injection Molding: Learn How to Get Started Now!
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts by injecting molten material into a mold. It is commonly used for producing plastic parts, but can also be used to produce parts made of metal, rubber, and other materials. The process is highly efficient, with the ability to produce large quantities of parts quickly and with high precision.
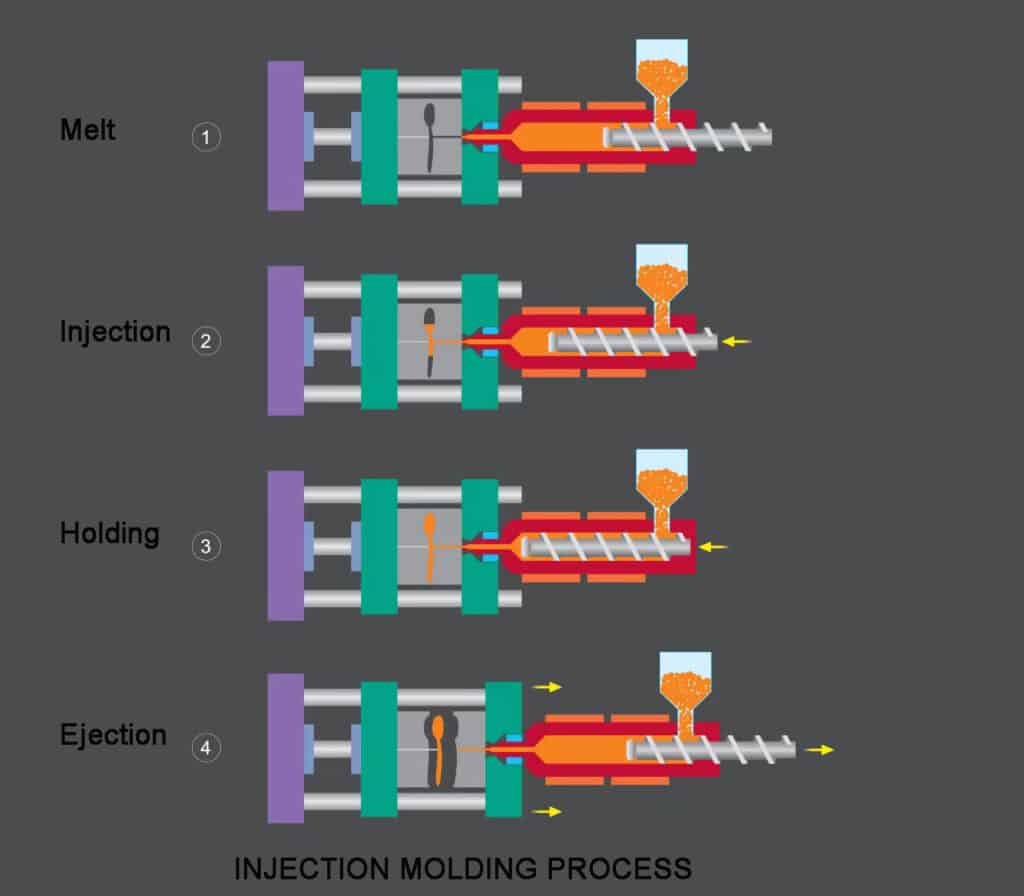
injection molding process
The injection molding process begins with the creation of a mold, which is a negative of the part that is to be produced. The mold is typically made of steel or aluminum and is precision machined to the desired shape. It is then mounted onto the injection molding machine, which consists of a hopper for the raw material, a heating unit to melt the material, a plunger or screw to feed the material into the mold, and a clamping unit to hold the mold in place during the injection process.
To begin the injection process, the raw material, typically a plastic resin, is fed into the hopper and heated to a molten state. The molten material is then injected into the mold under high pressure, where it cools and solidifies to take the shape of the mold. Once the material has cooled and solidified, the mold is opened and the part is ejected. The process is then repeated to produce additional parts.
benefits of injection molding
There are several benefits to using injection molding as a manufacturing process:
- High production rates: Injection molding is a highly efficient process that can produce large quantities of parts quickly and efficiently.
- Precision: The molds used in injection molding are highly accurate and can produce parts with tight tolerances.
- Automation: The process is highly automated, with the ability to produce large quantities of parts with minimal human intervention.
- Material versatility: Injection molding can be used to produce parts from a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, and rubber.
- Cost-effective: Injection molding is often a cost-effective option for producing large quantities of parts, as the upfront cost of the mold is offset by the high production rates.
- Complex shapes: Injection molding is well-suited for producing parts with complex shapes and features, such as ribs, bosses, and undercuts.
- High strength and durability: Injection molded parts are often strong and durable, making them ideal for use in demanding applications.
- Consistency: Injection molding produces parts that are consistent in terms of shape, size, and quality, making it a reliable option for producing high-quality parts.
different types of injection molding
There are several different types of injection molding, including standard injection molding, high-pressure injection molding, and micro injection molding. Standard injection molding is the most common type of injection molding and is used to produce a wide range of parts. High-pressure injection molding is used to produce parts with tight tolerances and high strength, while micro injection molding is used to produce small parts with fine details.
application
Injection molding is used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, medical, and consumer goods. It is particularly well-suited for producing large quantities of parts with complex shapes, such as automotive parts and medical devices. In addition, injection molding is often used to produce parts with high strength and durability, making it ideal for use in demanding applications.
design
There are a few key considerations to keep in mind when designing parts for injection molding.
- Material selection: Different materials have different properties and are suitable for different applications. It is important to select the appropriate material for the part being produced.
- Part design: The design of the part must take into account the flow of the molten material, as well as the cooling and solidification process. This includes considering features such as ribs, bosses, and undercuts, which can affect the flow of the material and the final shape of the part.
- Wall thickness: Maintaining consistent wall thickness is important for the integrity of the part. Thicker walls can add strength and durability, but also increase production time and cost.
- Draft angles: Injection molded parts often require draft angles to allow for easy removal from the mold. These angles should be considered in the design of the part to ensure that the part can be easily removed without damage.
- Parting lines: The location of the parting lines, or the points where the two halves of the mold meet, can affect the appearance and functionality of the part. It is important to consider the location of the parting lines in the design of the part.
- Tolerances: The desired tolerances of the part should be considered in the design process to ensure that the finished part meets the required specifications.
- Cooling: The cooling process is an important factor in the injection molding process and can affect the final properties of the part. It is important to consider the cooling process in the design of the part to ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications.
Overall, injection molding is a highly efficient and cost-effective manufacturing process that is widely used to produce a wide range of parts. Its ability to produce high precision parts with complex shapes and high strength makes it ideal for use in a variety of industries.