Fitting the Square Peg: The Art of Injection Mold Design
If you try to fit a square peg into a round hole. It doesn’t work right? This is the world of injection mold design. It’s not just about making a part, it’s about making a mold that fits the part—design and manufacturability in harmony.
In today’s manufacturing world designing for manufacturability is more important than ever. Let’s dive into the world of injection mold design and see what best practices can help streamline production, improve product quality and reduce cost.
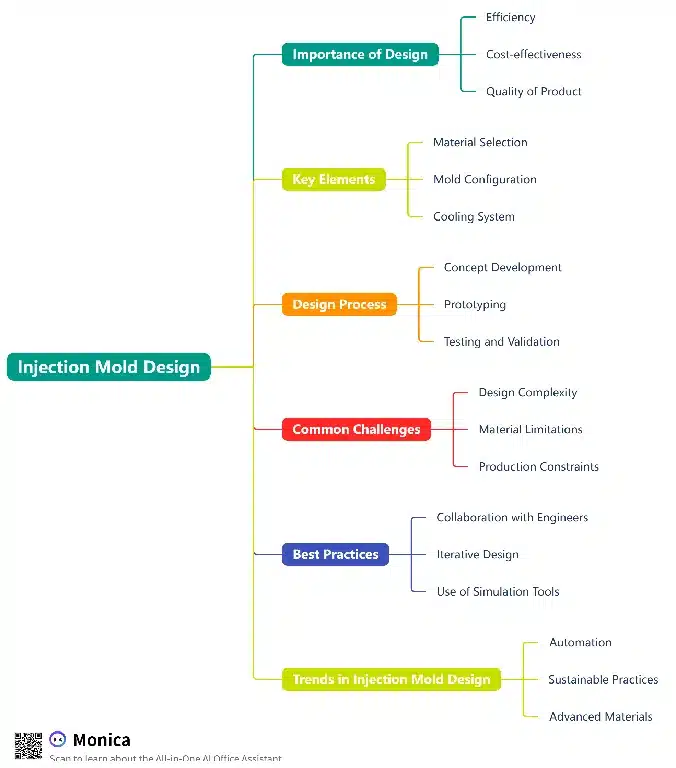
Injection Mold Design
Injection mold design is like writing a symphony. Every part of the design must work together to produce a perfect end product. At its core injection molding is simply injecting material into a mold cavity, allowing it to cool and solidify into the desired shape. It’s simple in theory but requires precise design to be efficient.
Molds are the behind the scenes heroes of product manufacturing, quietly shaping everything from toothbrushes to complex automotive parts. By understanding the intricacies of mold design manufacturers can avoid costly mistakes and ensure their final product meets the highest standards.
Designing for Manufacturability
Designing for manufacturability (DFM) is like building a house: the foundation must be strong and every detail planned. In the world of injection mold design DFM means considering all the factors to make the mold easy and economical to produce. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Geometric Complexity: Complex geometries look great but are a mold designer’s worst enemy. Simplify where you can to reduce defects and improve manufacturing efficiency.
- Tolerance Levels: Imagine trying to solve a jigsaw puzzle with pieces that don’t fit. Tolerance levels in mold design are critical for tight fits and high quality products.
- Parting Lines and Draft Angles: Parting lines and draft angles are like the seams in clothing—they ensure the part can be removed from the mold without damage. Proper design of these features is key to manufacturability.
Material Selection and Its Effects
Choosing the right material for your injection mold is like choosing the right ingredients for a recipe. The material affects everything from the life of the mold to the quality of the final product. Here are some of the factors to consider:
- Thermal Properties: Materials must be able to withstand the heat of molten plastic without deforming. Metals like steel and aluminum are used because of their thermal properties.
- Wear Resistance: Even the toughest materials can wear out with use. A wear resistant material ensures the mold will last over time.
- Cost: Quality vs cost is always a trade off. Some high performance materials may offer better qualities but come with a higher price tag.
Design for Molding
Think of your mold design as a well oiled machine. Every part must work together to be efficient. Here are some design considerations to consider:
- Gate Design: Gates are the entry points for the molten material to flow into the mold. Proper gate design ensures smooth flow and reduces defects like air pockets and flow lines.
- Cooling System: A well designed cooling system is like a car’s radiator, preventing overheating and ensuring consistent product quality. Good cooling reduces cycle times and increases productivity.
- Ejection System: Imagine baking a cake and trying to get it out of the pan. A good ejection system ensures the part can be removed from the mold easily and safely without damage and deformation.
Prototyping and Testing: The Loop
Prototyping is like rehearsing a play before opening night. It’s a critical step in mold design that allows for testing and refinement. Prototypes help identify design flaws and give insight into the molding process. Through the testing and feedback loop manufacturers can tweak their designs to get the final mold to perform optimally.
Common Issues and Solutions
Despite our best efforts, issues in injection mold design will arise. But these can be solved with:
- Warpage and Shrinkage: Like a cake that deflates after cooling, parts can warp or shrink if not designed properly. To fix this, designers can adjust material selection, mold design and processing parameters.
- Complex Geometries: To address complex geometries, using advanced simulation software can predict the problems and optimize the design.
- Tool Wear and Maintenance: Regular maintenance and choosing the right material can extend mold life and reduce wear related issues, keep production running smoothly.
Conclusion and Future of Injection Mold Design
In summary, designing for manufacturability in injection mold design is both an art and a science. By considering material selection, geometric complexity and cooling systems designers can get high quality products efficiently. As technology advances we will see trends like automation, simulation tools and eco friendly materials in the future of mold design. If we adopt these trends we will be ready for the challenges of tomorrow.
Q&A
- What is the most important thing in injection mold design? The most critical is that the design is manufacturable, which means balancing complexity, cost and quality to get a high quality product.
- How does material selection affect mold design? Material selection affects the durability, thermal properties and cost of the mold and has a big impact on the quality and efficiency of the process.
- Why is prototyping important in mold design? Prototyping allows testing and refinement of the mold design, helps to identify design flaws and ensures the final product meets the specifications.
- What are the common issues in injection molding? Common issues are warpage, shrinkage and tool wear. These can be managed by good design, material selection and regular maintenance.
- What will be the future trends in mold design? Automation, simulation tools and eco friendly materials will be the future trends which will drive innovation in mold design.